Glucose Screening Test During Pregnancy: Gestational Glucose Tolerance Test
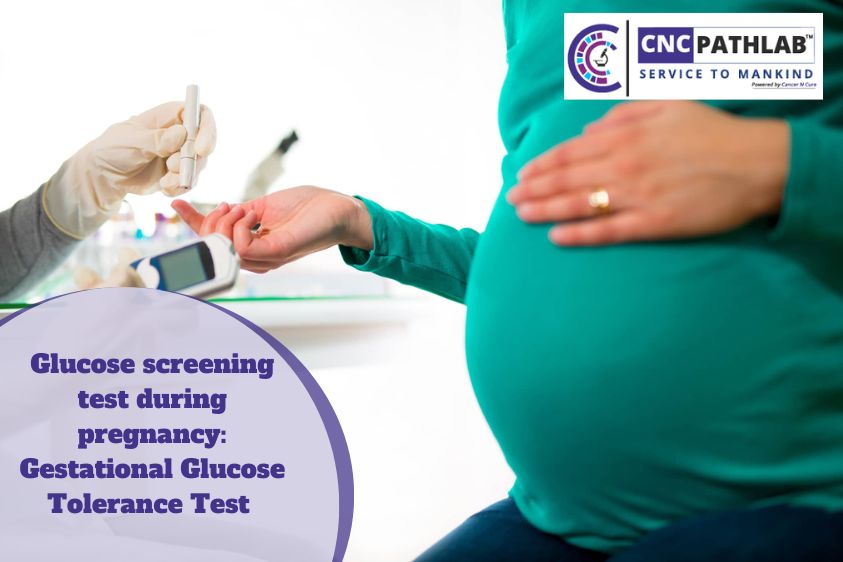
A glucose screening test is a routine test during pregnancy that checks a pregnant woman's blood glucose (sugar) level.
Gestational diabetes is high blood sugar (diabetes) that starts or is found during pregnancy.
The person may take a two-part test:
- Glucose screening test: The person has a blood test without fasting, then drinks a glucose drink and has another blood test one hour later. If the result is 140 mg/dL, the doctor may recommend a second test, the glucose tolerance test.
- Glucose tolerance test: The person will have a fasting blood test, then drink a glucose drink and have further blood tests 1, 2, and maybe 3 hours later.
If blood sugar levels are high, and the person has not had a diagnosis of diabetes before, the doctor will probably diagnose gestational diabetes.
WHAT IS GESTATIONAL DIABETES?
Gestational diabetes starts when the body is unable to make all of the insulin it needs for pregnancy.
Low insulin levels, combined with hormonal changes, can lead to insulin resistance. When this happens, high levels of glucose build up in the blood.
This can lead to the following complications:
- High blood glucose in the fetus and low levels after birth
- Difficulties during labor and the need for a cesarian delivery
- A higher risk of vaginal tearing during the birth and bleeding after delivery
- Risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future
Doctors usually recommend a glucose tolerance test between weeks 24–28 of pregnancy. Those with a higher risk may need a test earlier in the pregnancy.
How the Test is Performed?
TWO-STEP TESTING
- During the first step, you will have a glucose screening test:
- You do not need to prepare or change your diet in any way.
- You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose.
- Your blood will be drawn 1 hour after you drink the glucose solution to check your blood glucose level.
- If your blood glucose from the first step is too high, you will need to come back for a 3-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test:
- DO NOT eat or drink anything (other than sips of water) for 8 to 14 hours before your test. (You also cannot eat during the test.)
- You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose, 100 grams (g).
- You will have blood drawn before you drink the liquid, and again 3 more times every 60 minutes after you drink it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked.
- Allow at least 3 hours for this test.
ONE-STEP TESTING
- You need to go to the lab one time for a 2-hour glucose tolerance test. For this test:
- DO NOT eat or drink anything (other than sips of water) for 8 to 14 hours before your test. (You also cannot eat during the test.)
- You will be asked to drink a liquid that contains glucose (75 g).
- You will have blood drawn before you drink the liquid, and again 2 more times every 60 minutes after you drink it. Each time, your blood glucose level will be checked.
- Allow at least 2 hours for this test.
Most people do not experience any side effects from glucose testing, and serious complications are rare.
As it involves fasting and blood testing, the glucose tolerance test might cause nausea, light-headedness, shortness of breath, and sweating in some people.
The doctor uses a needle to draw the blood, so the injection may cause moderate pain for some.
More serious but less common risks include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting
- Blood collection under the skin
- Infection

.jpg)

.jpg)
